Brain and Skull Terms
Anterior fontanelle
Refers to the “soft spot” toward the front of the top of an infant’s head between the growing skull bone.
Brain
Refers to the body’s thought and activity center which gathers outside information through the 5 senses, processes the data into thoughts, words, and actions, and causes direct and indirect motor responses for movement and learning. The brain also controls the ‘automatic’ body functions such as breathing, digesting, and pumping blood.
Forebrain
Refers to the front section of the developing baby’s brain, functions as the sense’s control and processing center, and controls involuntary movement and activities.
Hindbrain
Refers to the back section of the developing baby’s brain; as your child grows up, it takes on the job of controlling automatic tasks and balance.
Cerebellum
Refers to the largest section of the brain, in charge of muscle coordination and balance; it’s located right between the brain’s stem and the back of the cerebrum.
Cerebral Hemispheres
Refers to the two large, convoluted, side-by-side sections of the brain, inside the skull case.
Chiari malformation
Refers to a rare inherited deformity in which the brainstem and cerebellum are too long, pushing themselves down into the spinal canal. This causes too much pressure on the tissues and prevents normal spinal fluid flow.
Corpus Callosum
Refers to the big bundle of fibers and other tissue shaped into a band, located between the two cerebral hemispheres.
Cranial Fossa
Refers to the floor of the skull, containing three depressions – front, middle, and back. Each holds and protects a different set of brain sections: the depressed area toward the back of the brain (posterior) holds the cerebrum, pons, and medulla oblongata; the second depressed area holds the temporal lobes on the sides and the hypothalamus in the middle; the frontal area contains the frontal lobes of the brain.
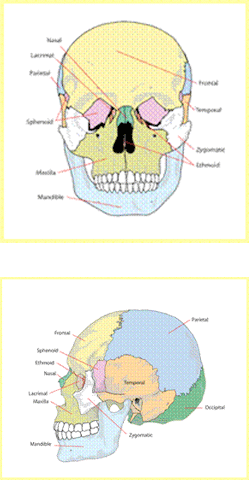
Cranium
Refers to the ‘case’ or skull that holds and protects the brain; 8 bones connect at each side with inflexible sutures to form the protective top, side and back of the adult skull; 14 bones in the front of the head form the facial structures and tissue/tooth support.
Fornix
Refers to the nerve fiber bundle just underneath the corpus callosum; the nerves stay continuously busy sending information, then receiving responses from the hippocampus and from the rest of the brain.
Fusion
Refers to the natural process of gradual closure of flexible sutures in your infant’s skull; the sutures are connected by a thin line of flexible cartilage to allow rapid brain growth in the womb and for a short while after birth; as brain growth slows, the skull sutures ‘fuse’ to create an even more permanently protective ‘brain case’.
Hippocampus
Refers to the long, curved ridge in the brain, in charge of creating, keeping, and processing memory-related thoughts. It’s made of gray matter layered under white matter, connected to each of the two side ventricles or pocket areas.
Hydrocephalus
Refers to a condition of excess spinal fluid buildup in or on the brain: hydro= fluid, water; cephalus= having to do with the brain or head.
Lobes
Refers to the rounded segments of the brain.
Medulla Oblongata
Refers to the long, descending segment of the brain connecting the spinal cord and fourth ventricle; it holds major nerves and fibers linking the spinal cord to areas in charge of more complex activities, including involuntary tasks.
Occipital
Refers to a four-part bone in the back of the skull shaped like a curved trapezoid.
Pituitary Gland
Refers to a reddish-gray hormone-production organ hanging underneath the lower middle segment of the brain; in charge of the body’s growth and development rate, other hormone-production organs’ activation, smooth muscle activation, kidney function, and reproduction.
Plate
Refers to a single unit or segment of flat, thin, bony segments that make up your child’s skull; the plates are connected along their sides by flexible sutures to allow the child’s rapidly growing brain to reach a close-to-adult size, until the brain no longer needs such flexibility.
Pons
Refers to a wide band of nerve fibers found in front of the medulla oblongata and underneath the cerebellum; it’s in charge of information transfer.
Posterior
Refers to the back of an object, or the back area of a space.
Suture
Refers to the flexible joined areas of the skull plates making up the skull; each suture fuses, holding the skull plates firmly in position at a specific point in development; some closing after birth. When plate fusion occurs too early in development, it imposes pressure on the growing brain, becoming the condition we call “Craniosynostosis”. We name sutures according to their location on the skull/head.
Suture has another meaning, unrelated to skull plates: in surgery, ‘suture’ refers to a stitch the surgeon makes to close the area of repair after a procedure.
Ventricle
Refers to one of a series of interconnected pouch-like structures in the brain, allowing messages to travel from the spinal cord to various brain centers.